Having ability to create a on demand local Postgres server in docker container is very beneficial for any application developer who wants to run or develop any application locally which is dependent on Postgres server.
I will discuss how to do that is very simple steps.
Step 1: Create a Docker file
Create a folder and and create a file with name Dockerfile with following contents.
FROM Postgres
ENV POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mypassword1
ENV POSTGRES_DB=dept
COPY employee.sql /docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/
The above file will do the following
It will use postgres base image which comes with Postgres server
Sets two environment variables POSTGRES_PASSWORD which will have the password to the container set as mypassword1 and POSTGRES_DB which which tells that the database name will be dept.
The last line copies a file containing sql script to the directory docker-entrypoint-initdb.d
We will see the contents of this script file next but the reason we have copied this file is that any sql script which is copied here also gets executed automatically in the server database.
Step 2: Create a sql script
Create a file called employee.sql in the same directory where Dockerfile is created with the following content
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS employee (
employee_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50)
);
INSERT INTO employee(employee_id, name) values(1, 'John');
INSERT INTO employee(employee_id, name) values(2, 'Vinny');
INSERT INTO employee(employee_id, name) values(3, 'Cathy');
employee_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50)
);
INSERT INTO employee(employee_id, name) values(1, 'John');
INSERT INTO employee(employee_id, name) values(2, 'Vinny');
INSERT INTO employee(employee_id, name) values(3, 'Cathy');
Step 3: build the docker image with following command
Run the following command in the same folder where Dockerfile was created. This will create a image for Postgres with environment variables you want along with sql script.
docker build . -t employeedb
Step 4: Run the container
docker run -d --name empdb -p 5432:5432 employeedb
The above command runs the docker run in background mode (-d), sets name of the container to empdb (this can be used when you want to stop the container) -p sets the port to 5432 and maps to docker on 5432 where Postgres server is running and finally mentions the image name employeedb which was created in the previous step.
Step 5: Verify the container was successfully started and is running
docker container lsYou should see response similar to following
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
05243a35e918 employeedb "docker-entrypoint.s…" 14 seconds ago Up 14 seconds 0.0.0.0:5432->5432/tcp empdbStep 6: Connect with Client and check Verify
I have used PGAdmin client but you can use any other client too including docker command line. Use the following values
host: localhost
user id: postgres (This is default user)
password: mypassword1 (same as the environment value POSTGRES_PASSWORD mentioned in docker file)
database: dept (same as the environment value POSTGRES_DB mentioned in docker file)
Once connected you can run select command and verify the rows in the table.
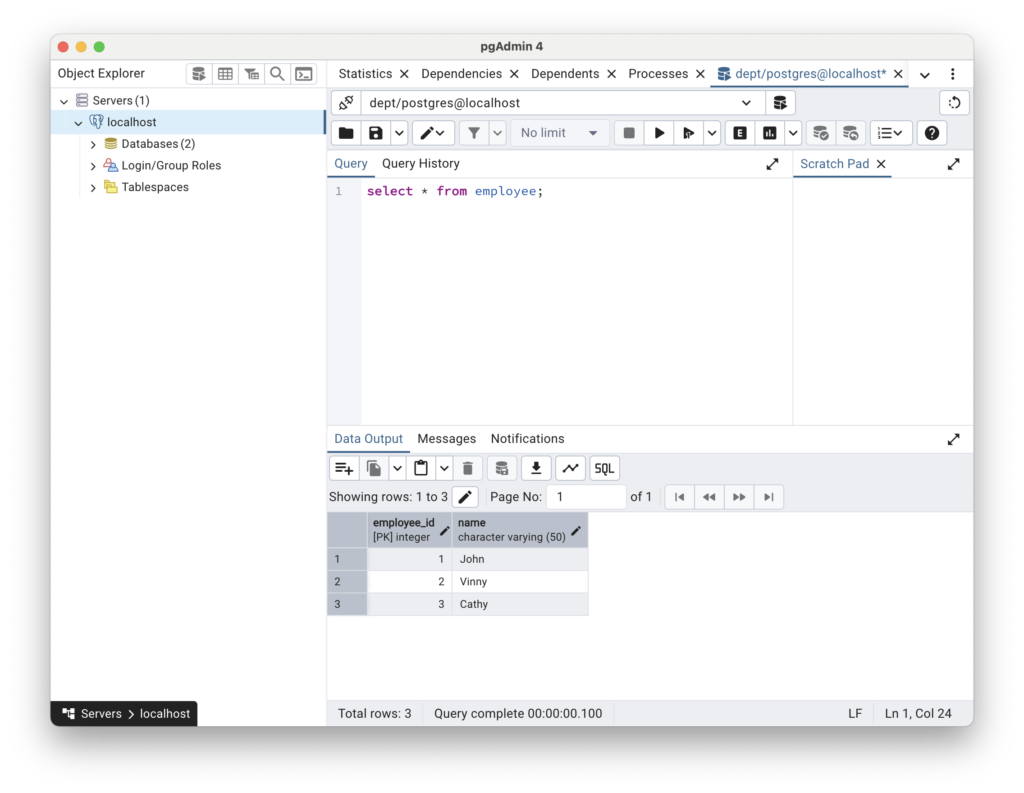
If you want to watch me do the above steps in video you can watch that on YouTube
Leave a Reply